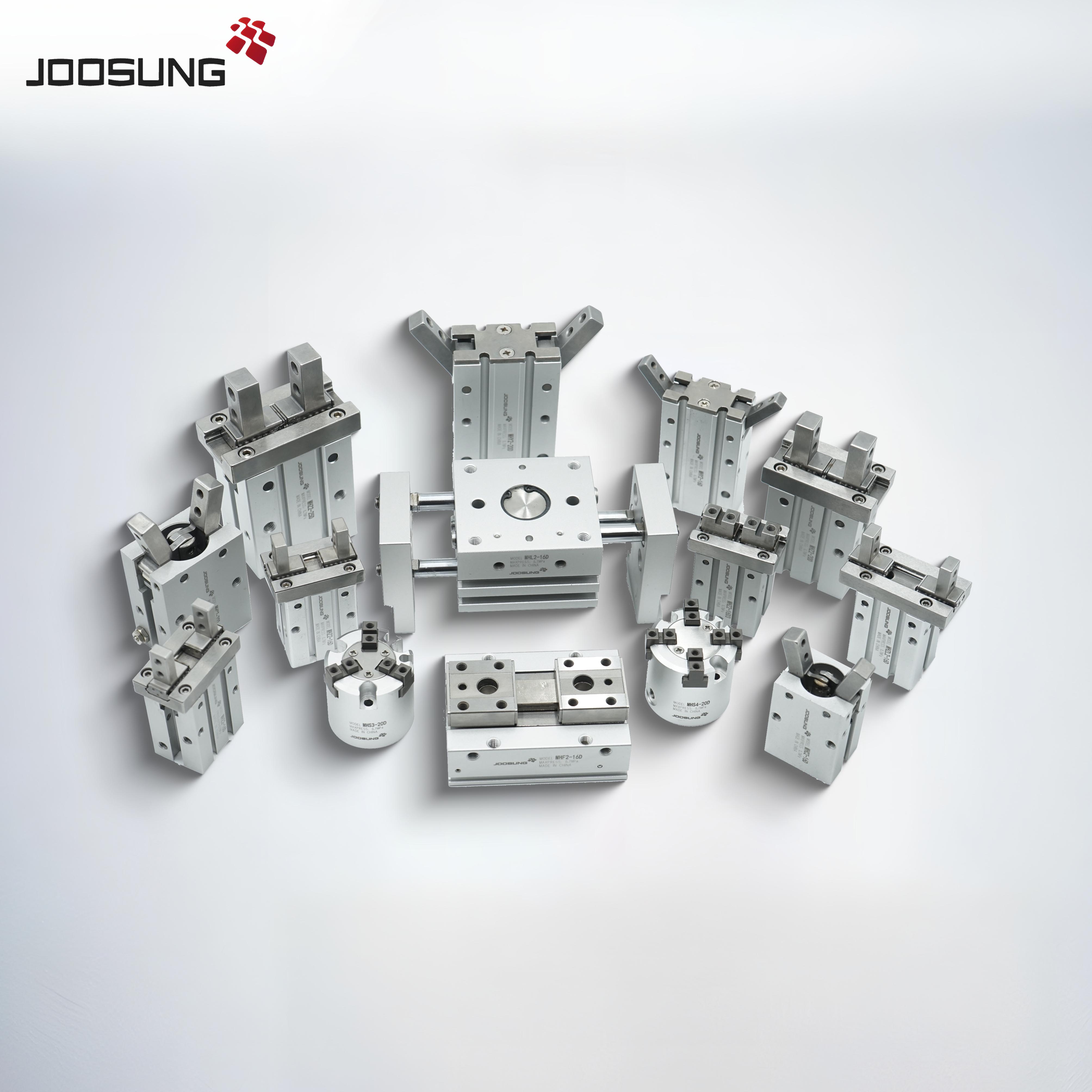
An ACQ extremely-skinny Pneumatic Cylinder is a specialized kind of pneumatic cylinder designed to be extremely compact and light-weight while nevertheless handing over powerful overall performance for various automation and business packages. The "ACQ" designation usually refers to a particular collection or version by means of a producer (like SMC or Airtac), but the wellknown capabilities of extremely-skinny pneumatic cylinders are similar throughout manufacturers.
Key characteristics:
extremely-thin Profile:
The defining function of these cylinders is their narrow and compact design. they are frequently utilized in applications where area is constrained and a conventional pneumatic cylinder with a larger diameter could be impractical.
these cylinders might also have a diameter this is thinner than popular cylinders, ranging from some millimeters to 3 centimeters.
lightweight production:
due to their compact design, these cylinders are commonly lighter, which can be high-quality in lowering the general weight of a robotic arm, conveyor system, or other moving elements in automation.
excessive Precision:
ultra-thin pneumatic cylinders are constructed for excessive precision and smooth linear movement. This makes them ideal for delicate responsibilities along with choose-and-vicinity operations, scientific device manufacturing, or programs where specific manipulate is crucial.
versatile Mounting:
those cylinders may be hooked up in one-of-a-kind orientations or on small equipment, permitting them to healthy into tight or hard-to-reach places.
materials:
often crafted from anodized aluminum or excessive-energy materials that make sure sturdiness without sacrificing the light-weight nature.
how it Works:
Pneumatic cylinders work with the aid of the use of compressed air to create movement. here is a primary breakdown of ways the ACQ ultra-thin pneumatic cylinder operates:
Air supply:
Compressed air is provided to the cylinder thru an inlet valve. This air strain acts on the piston within the cylinder.
Piston movement:
The compressed air forces the piston within the cylinder to transport. The piston is generally connected to a rod (the actuator) that converts this movement right into a linear displacement.
Double-acting or unmarried-acting:
Double-performing Cylinder: Air pressure is implemented to each facets of the piston, allowing it to move in each guidelines.
unmarried-acting Cylinder: Air pressure is carried out to only one facet of the piston, with a spring on the opposite side to return the piston to its starting function as soon as the air strain is launched.
manipulate:
The movement of the piston is managed via solenoid valves, which alter the float of compressed air into and out of the cylinder. This lets in for unique control of the cylinder’s extension and retraction.
go back Mechanism:
In a few models, specifically single-appearing cylinders, a spring or outside mechanical system guarantees the cylinder returns to its original role after the air deliver is grew to become off.
applications:
Robotics: For compact actuators that want unique and smooth linear motion.
automated equipment: In structures wherein area constraints require slim and efficient actuators.
scientific devices: utilized in programs wherein a small size, light weight, and precision are necessary, including in surgical robots or testing equipment.
Packaging and meeting traces: To carry out moves like pressing, lifting, or transferring objects in a restrained space.
basic, an ACQ ultra-skinny pneumatic cylinder is an efficient answer for programs requiring a aggregate of small shape thing and reliable pneumatic performance.