Pneumatic valve Solenoid valve operating principle and function of designated explanation
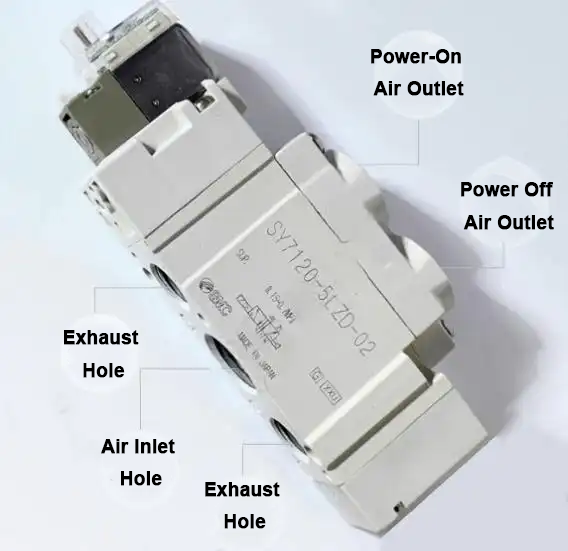
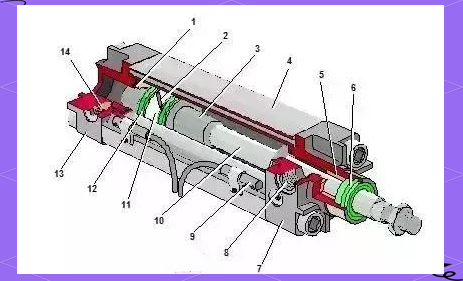
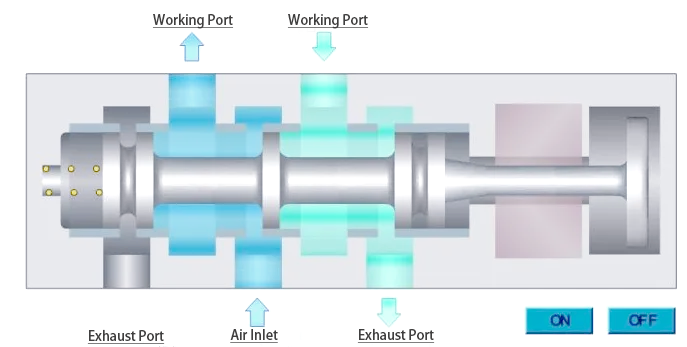
Pneumatic valve, as an crucial fluid manipulate gadget in commercial pipelines, its middle additives include pneumatic actuators and valves. by using compressing natural air to pressure valve movement, pneumatic valves can quick and precisely manage the go with the flow and blocking of pipe intermediaries, making them perfect for quick reduce-off operations. further, pneumatic valves are ready with an expansion of accessories which include solenoid valves, air deliver managing triples, restrict switches, positioners, and manipulate bins to aid the needs of subject manage and faraway centralized manage. particularly for two-role valves that best need to open and near, the solenoid valve is an vital part. through the process of excitation and demagnetization, the solenoid valve achieves correct manage of the outlet and final of the pneumatic valve. In terms of the air direction (or liquid path), the 2-position 3-manner solenoid valve layout has an intake hollow, an outlet hollow and an exhaust hollow, even as the two-role 5-way solenoid valve provides a high quality action vent and a reactionary action vent, in addition to the corresponding fantastic movement and anti-motion exhaust holes. For small automatic control gadget, 8~12mm industrial rubber gas pipe is usually selected because the gasoline pipe cloth.

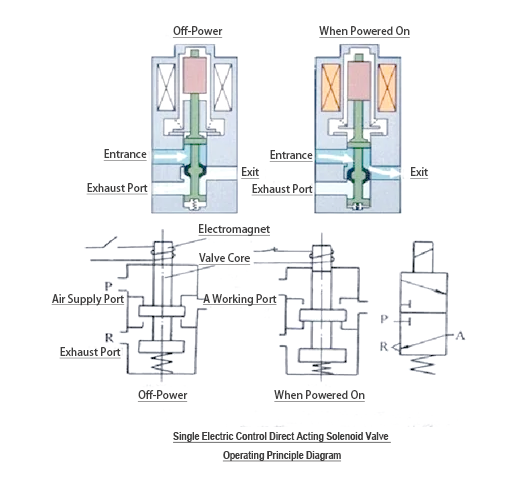
In phrases of electrical control, the two-role 3-manner solenoid valve usually uses a single electronic manage layout, this is, a unmarried coil, whilst the two-role 5-way solenoid valve in most cases uses a double electronic manipulate layout, this is, a double coil. The coil voltage level of those solenoid valves is commonly selected DC24V, AC220V, and so forth. -position 3-way solenoid valve can be divided into typically closed type and usually open type, of which generally closed type manner that the gas path is disconnected inside the country of no power, and typically open kind is the alternative, the fuel route is attached whilst there may be no electricity.
Next, permit's take a better take a look at the operation precept of these sorts of -function three-manner solenoid valves:
(1) generally closed -role three-way solenoid valve: whilst the coil is energized, the gasoline route is connected; once the coil is powered off, the gasoline route might be disconnected, that's much like the "factor" manipulate.
(2) commonly open -position three-manner unmarried electronically controlled solenoid valve: its running principle is the opposite of the commonly closed kind, this is, the gas direction is disconnected whilst the coil is powered on, and the gas direction is hooked up when the energy is off, and the "point" manipulate is also finished.

The operation principle of the two-function five-manner double-managed solenoid valve is: when the effective acting coil is energized, the advantageous performing gas path may be connected (this is, the high quality performing vent will have gas output). Even after the fine acting coil is powered off, the fantastic acting gasoline course will remain related until the anti-appearing coil is powered on. similarly, while the counteracting coil is energized, the counteracting gasoline path is switched on (that is, there may be a fuel output from the response generating hole). After the electricity is turned off, the reverse appearing gas direction may even stay connected until the positive acting coil is energized again. This feature makes the two-position 5-manner dual-controlled solenoid valve have a "self-locking" feature, similar to the memory function.
inside the design of the electromechanical manipulate loop or the preparation of the % software, this feature of the two-role five-manner double-controlled solenoid valve may be used to most effective permit the solenoid valve coil to operate for 1 to 2 seconds, which will successfully protect the solenoid valve coil and increase its carrier life.
subsequent, allow's look at the precept of a unmarried electronically controlled solenoid valve. The unmarried solenoid valve drives the movement of the spool by means of controlling the cutting-edge wreck of the solenoid coil and the movement of the spring, after which controls the hole and ultimate of the valve.
When the right coil is energized, the left spring is compressed:
The coil at the left is powered, and the spring on the right is compressed: in a unmarried electronically controlled solenoid valve, when the coil on one facet is powered, the spring on the facet might be compressed due to the motion of the electromagnetic force. that is the simple operating precept of a unmarried electronically managed solenoid valve.
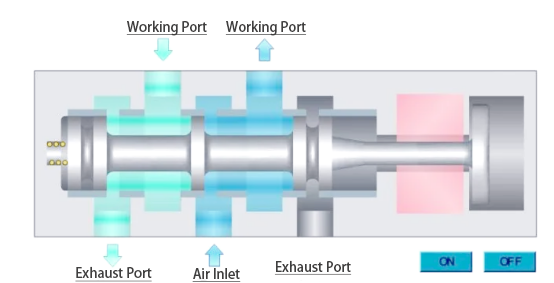
In a unmarried electronically managed solenoid valve, when the coil at the right loses modern-day, the spring on the left will get better due to the disappearance of the electromagnetic pressure, this is, enlarge out. that is every other vital operating characteristic of a single electronically controlled solenoid valve.
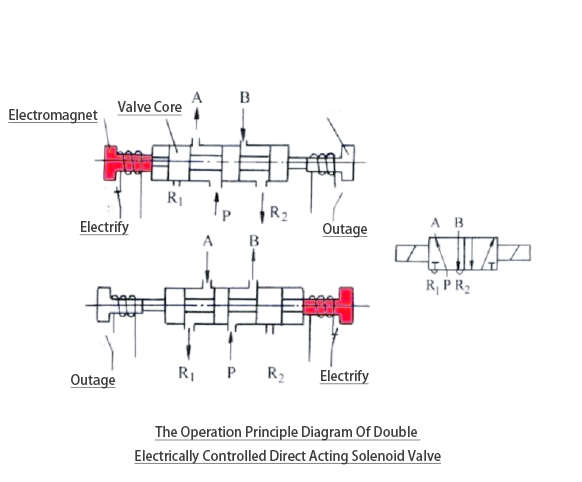
B Double electric powered manipulate schematic
The precept of double electronically controlled solenoid valve is that the solenoid coil on each aspects can manage the hole and closing kingdom of the valve by means of switching between strength and electricity loss. while one coil is out of strength and the alternative isn't always but powered, the spool can continue to be stationary, which makes the dual-controlled solenoid valve have a memory characteristic.
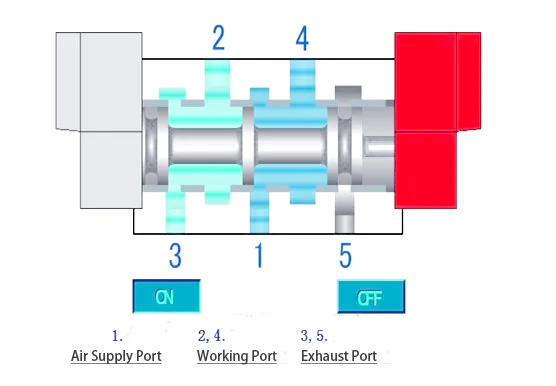
when the proper electromagnetic coil loses electricity and the left electromagnetic coil receives strength, the spool will continue to be stationary, that's the result of the reminiscence characteristic of the double electronically managed solenoid valve.
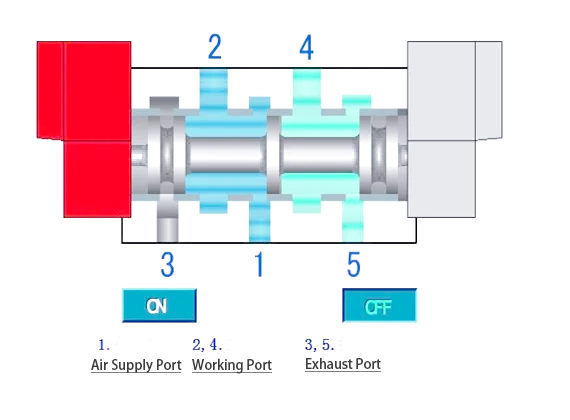
When the left electromagnetic coil loses electricity and the right electromagnetic coil receives power, the spool will circulate to the proper until it reaches the right restrict position. this is because of the switching characteristic of the double electronically managed solenoid valve in motion.
The pneumatic actuator is powered by means of compressed air and drives the pneumatic actuator via changing the input manage signal into a pressure signal, as a way to understand non-stop adjustment or switch manage of the valve. further, the pneumatic manage valve also can be geared up with an expansion of add-ons to attain a diffusion of manipulate capabilities to completely meet the particular needs of the manipulate system for the pneumatic manipulate valve. those accessories make the feature of the pneumatic manipulate valve greater ideal, affordable and complete.