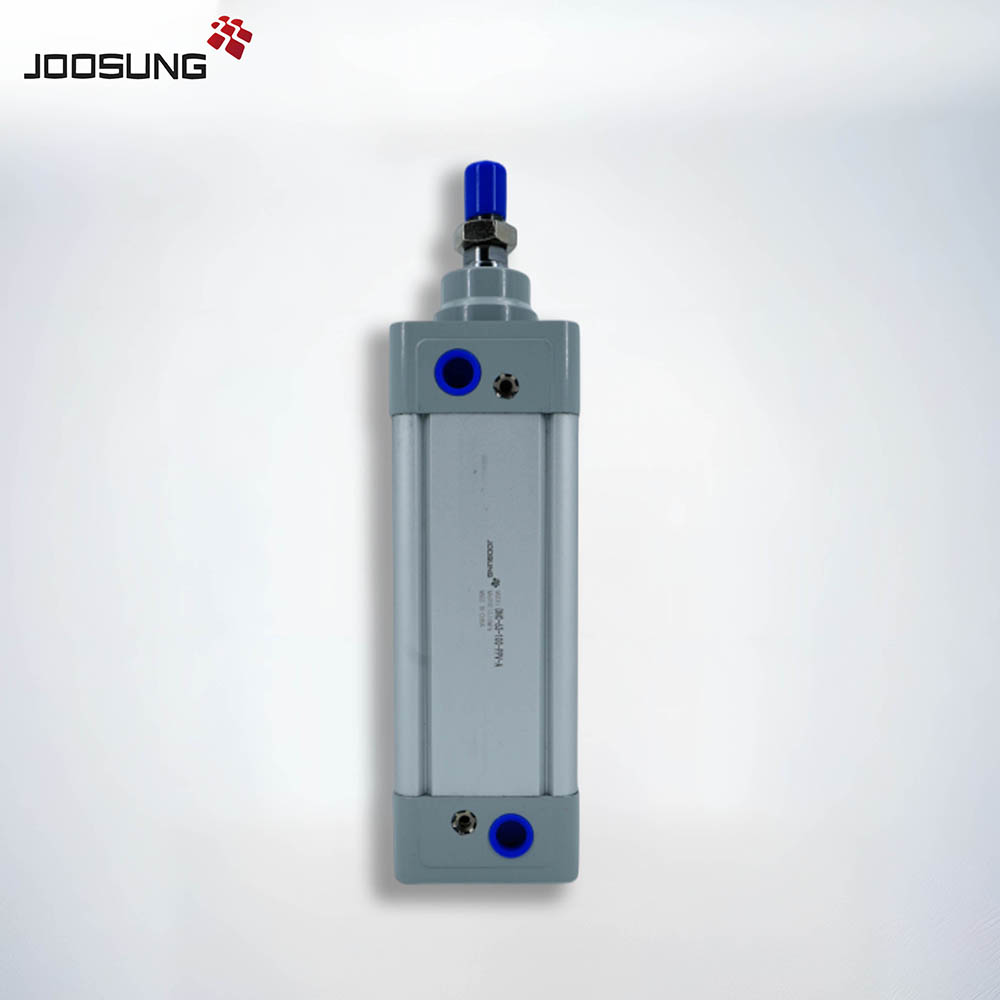
A double-performing pneumatic cylinder presents pressure in each guidelines by using the usage of compressed air to move the piston in opposite strokes—one for extension and one for retraction. right here’s the way it works:
1. Air Ports for Bidirectional control
The cylinder has air ports: one at every cease.
with the aid of alternating the deliver of compressed air among these ports, the piston movements in each directions.
2. Extension Stroke (forward motion)
Compressed air enters the port at the rear side of the cylinder.
The stress forces the piston forward, extending the piston rod outward.
on the identical time, the front air chamber vents out the air.
3. Retraction Stroke (Backward motion)
Compressed air enters the port on the the front facet of the cylinder.
The stress pushes the piston backward, retracting the piston rod.
The rear chamber vents out air, permitting easy movement.
4. pressure technology in both guidelines
The force generated depends at the air pressure (P) and piston place (A):
force = pressure × region (F = P × A)
The pressure within the extension stroke is typically extra than within the retraction stroke due to the fact the piston rod reduces the powerful area at the retraction side.
5. precise manage with Valves
A four-way directional manage valve is generally used to interchange air deliver between the 2 ports.
glide manipulate valves can modify velocity, and cushioning mechanisms help smooth operation.
Key benefits
permits push and pull movements with out external springs.
affords continuous, controlled movement in both directions.
suitable for automation, robotics, and business applications requiring reliable bidirectional force.
via the use of compressed air in an alternating cycle, a double-performing pneumatic cylinder achieves forceful and managed motion in each instructions.