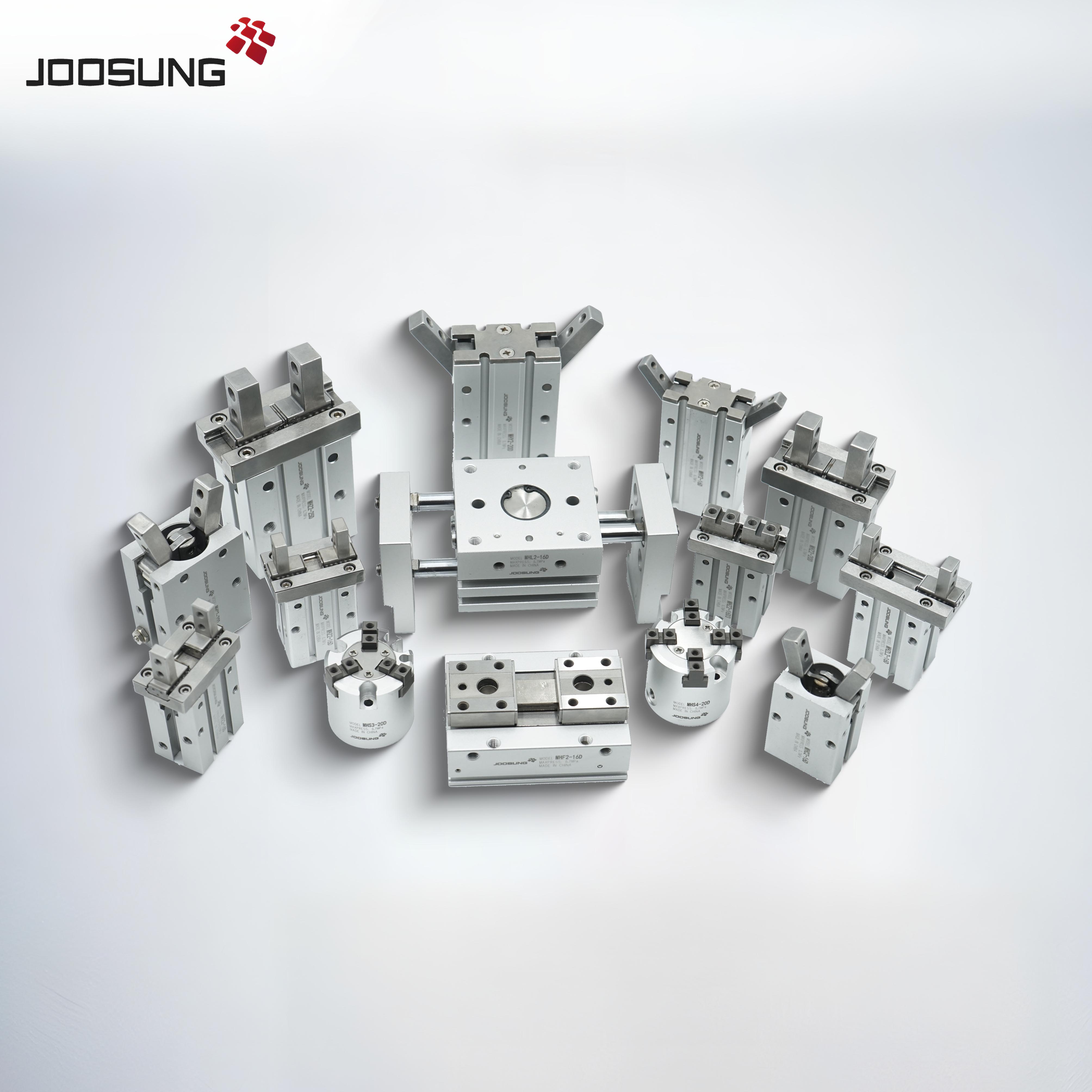
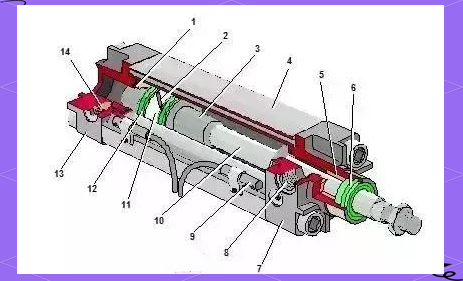
The piston in a double-acting pneumatic cylinder performs a critical function in converting compressed air electricity into linear mechanical motion. Its main features include:
1. producing Linear motion
The piston movements to and fro within the cylinder whilst compressed air is alternately supplied to either facet.
This motion is used to carry out obligations along with pushing, pulling, lifting, or pressing.
2. Dividing Air Chambers
The piston separates the cylinder into two air chambers (one on each aspect of the piston).
Compressed air enters one chamber at the same time as the alternative side vents, permitting managed motion in each guidelines.
3. Transmitting force
The pressure of compressed air acts at the piston floor, creating force that moves the piston rod.
The force generated relies upon on air strain and piston surface location.
4. permitting precise control
by adjusting the air strain and float price, the piston’s speed, pressure, and path may be precisely controlled.
This makes it beneficial for packages requiring constant and smooth movement.
5. supplying a Sealing Barrier
The piston incorporates seals (O-earrings or cup seals) that prevent air leakage between the 2 chambers.
This ensures green operation by way of preserving air pressure balance within the cylinder.
In summary, the piston in a double-acting pneumatic cylinder converts compressed air into bidirectional linear motion, permitting efficient and controlled mechanical operations.