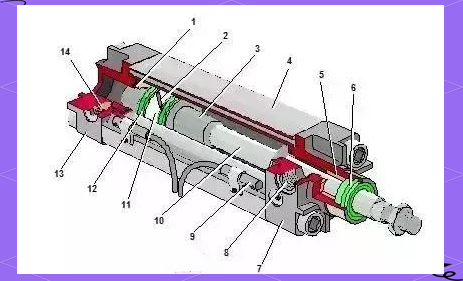
SY series pneumatic solenoid valves are widely used for controlling airflow in various pneumatic systems. However, like any mechanical or electrical component, they can experience common issues that may affect their performance. Below are some of the typical problems you might encounter with **SY series pneumatic solenoid valves**, along with their potential causes and solutions:
### 1. **Valve Does Not Activate**
- **Cause: Electrical Issues**
- **Power Supply Issues:** If the solenoid coil does not receive the correct voltage or current, the valve will not actuate. This could be due to wiring problems, a blown fuse, or issues with the power supply.
- **Solution:** Verify the voltage and current ratings for the solenoid coil match the electrical power supply. Check for loose wires, faulty relays, or damaged fuses, and ensure the connections are secure.
- **Cause: Faulty Solenoid Coil**
- **Worn-out or Burnt-out Coil:** Over time, solenoid coils can degrade or burn out due to prolonged use or power surges.
- **Solution:** Inspect the coil for signs of damage, such as discoloration or cracks. If the coil is faulty, replace it with a new one that matches the specifications.
### 2. **Air Leakage**
- **Cause: Seal or O-Ring Failure**
- **Worn or Damaged Seals:** The O-rings or seals inside the valve can wear out or become damaged, leading to air leakage at the valve ports.
- **Solution:** Inspect the seals and O-rings for wear or damage. Replace any worn-out seals or O-rings to ensure an airtight seal.
- **Cause: Improper Installation**
- **Incorrectly Assembled Valve:** If the valve parts are not assembled correctly, or if there is excessive torque applied to the valve during installation, it can cause leaks.
- **Solution:** Disassemble the valve, check the assembly, and ensure that all parts are installed correctly. Tighten connections as per the manufacturer's torque specifications.
### 3. **Inconsistent Valve Operation**
- **Cause: Contaminants in the Valve**
- **Dirt, Dust, or Debris:** Particles such as dust, dirt, or other contaminants can enter the valve through the air supply, causing the valve to stick or operate inconsistently.
- **Solution:** Install filters in the air supply to prevent debris from entering the valve. Clean the valve and check for any blockages or debris inside. Replace any damaged internal parts, such as the valve seat or spring.
- **Cause: Internal Component Wear**
- **Worn Internal Parts:** Over time, internal components like the valve spool, seals, or springs can wear out, leading to inconsistent operation or improper sealing.
- **Solution:** Regularly inspect and maintain the valve. Replace any worn-out internal parts such as the spool, spring, or seals.
### 4. **Valve Fails to Close or Sticks Open**
- **Cause: Solenoid Coil Failure**
- **Failure to Energize or De-Energize:** The solenoid coil may not properly energize or de-energize due to electrical issues, causing the valve to fail to close or stick open.
- **Solution:** Check the electrical connections, test the solenoid coil for proper operation, and verify the control signal to ensure it is functioning correctly.
- **Cause: Air Supply Issues**
- **Insufficient Air Pressure:** Low or fluctuating air pressure can prevent the valve from closing properly, as the actuator may not have enough force to move the valve's internal components.
- **Solution:** Verify that the air supply pressure is within the recommended operating range for the valve. Adjust the air compressor or regulator to ensure consistent pressure.
### 5. **Slow Response Time**
- **Cause: Incorrect Valve Size**
- **Undersized Valve:** An undersized valve may not allow enough air flow to meet the required actuation speed, leading to slow response times.
- **Solution:** Check that the valve size (Cv value) is appropriate for the application and flow requirements. If necessary, replace the valve with one that has a higher flow capacity.
- **Cause: Internal Blockages or Restriction**
- **Clogged Valve Ports:** Blockages in the valve ports or within the valve body can restrict airflow, slowing down the response time.
- **Solution:** Disassemble the valve and inspect it for any internal blockages. Clean or replace the affected components as needed.
### 6. **Valve Chatters or Vibrates**
- **Cause: Air Pressure Fluctuations**
- **Excessive or Fluctuating Air Pressure:** If the air pressure is too high or fluctuates significantly, it can cause the valve to chatter or vibrate.
- **Solution:** Check the air pressure regulator to ensure stable and consistent pressure. Adjust the pressure if necessary to match the valve's rated pressure range.
- **Cause: Incorrect Pilot Pressure**
- **Incorrect Control Signal:** A low or fluctuating pilot pressure can cause improper operation of the valve, leading to chattering.
- **Solution:** Verify that the pilot control signal matches the valve's specifications and is stable.
### 7. **Valve Will Not Shut Off (Continuous Flow)**
- **Cause: Valve Sticking in Open Position**
- **Sticky or Seized Internal Components:** Dirt, moisture, or wear on the valve internals can prevent the valve from fully sealing when it is supposed to close.
- **Solution:** Clean and inspect the valve internals. Replace any worn-out parts, such as the sealing components or valve spool.
- **Cause: Electrical Signal Issue**
- **Failure to De-Energize:** If the valve is not de-energizing correctly, it could remain in the open position.
- **Solution:** Check the electrical control circuit for faults, such as broken wires or faulty relays.
### 8. **Excessive Power Consumption**
- **Cause: Faulty Solenoid Coil**
- **Shorted Coil or Incorrect Voltage:** A shorted or improperly sized solenoid coil can draw excessive current and power.
- **Solution:** Check the coil's resistance and ensure that it is operating within the rated voltage and current specifications.
- **Cause: Constant Operation**
- **Continuous Energizing:** If the solenoid is continuously energized (even when not needed), it will draw power constantly, leading to energy inefficiency.
- **Solution:** Verify that the control system is properly managing the energizing and de-energizing of the solenoid to avoid unnecessary power consumption.
### Conclusion:
The most common problems with **SY series pneumatic solenoid valves** are related to electrical issues, air supply problems, and wear or contamination of internal components. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and monitoring of system conditions can help prevent these issues. When problems do arise, a thorough diagnosis and replacement of faulty parts can often restore the valve's proper function.