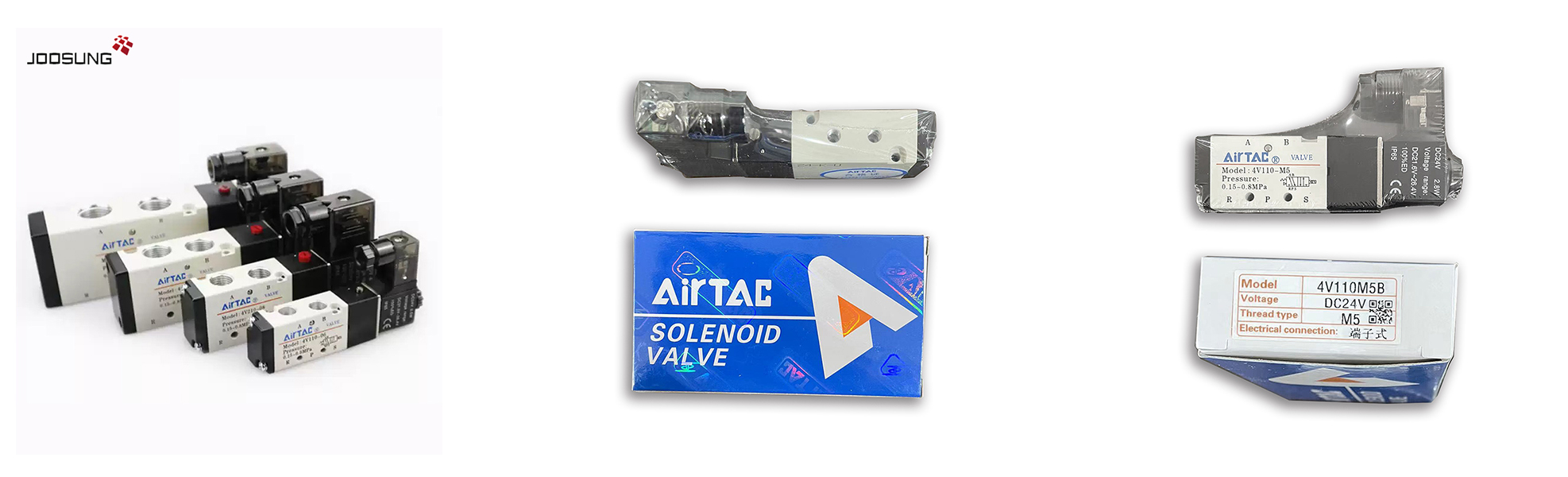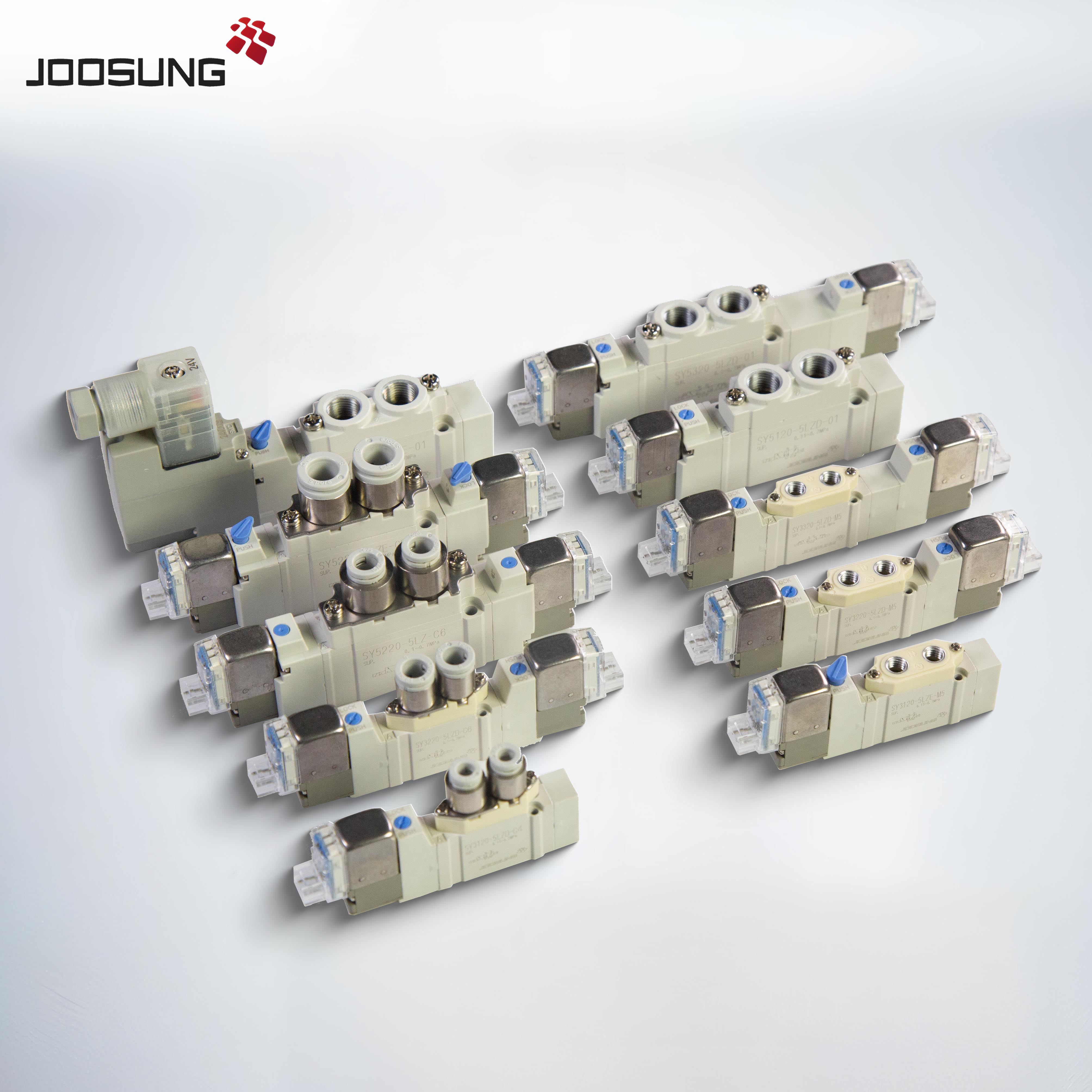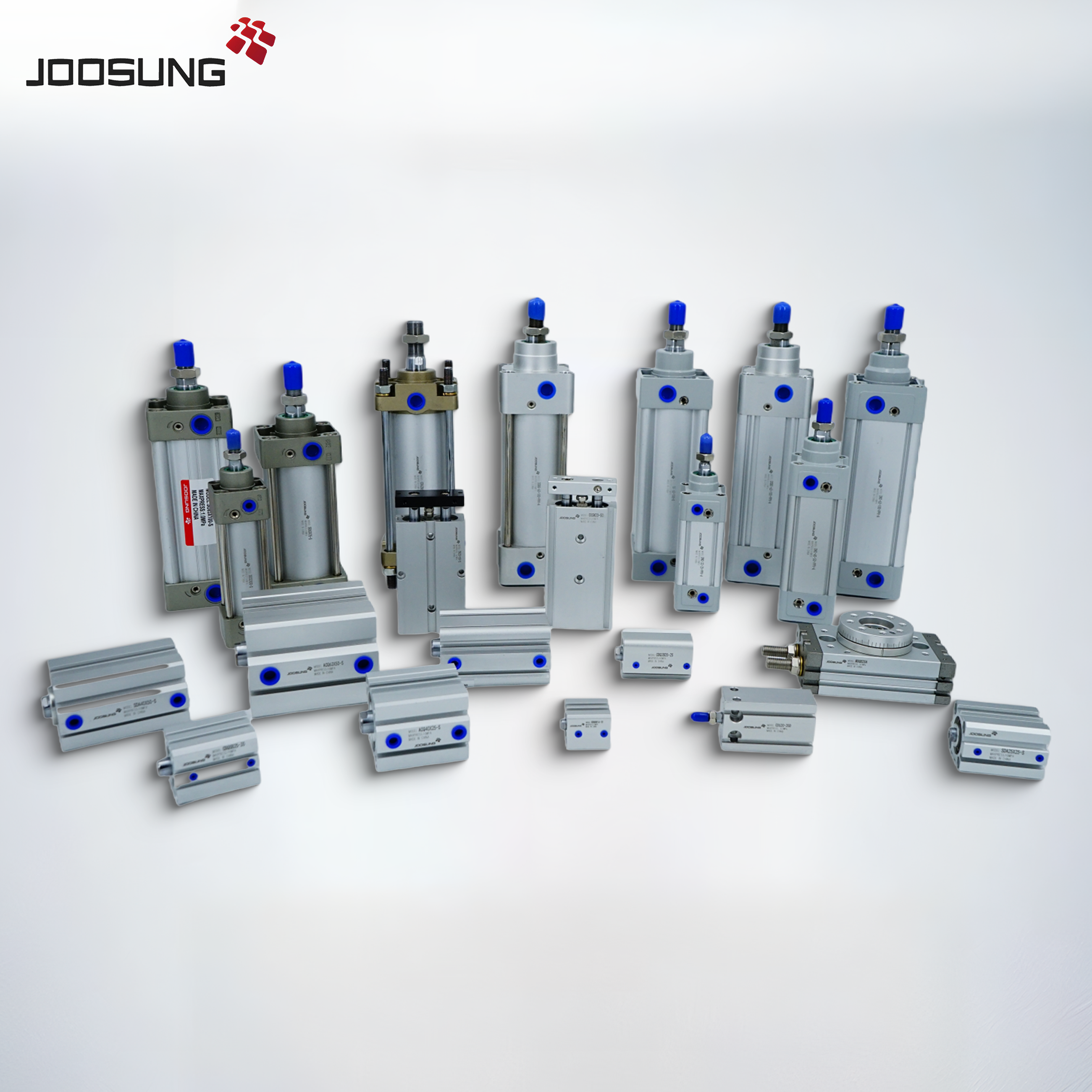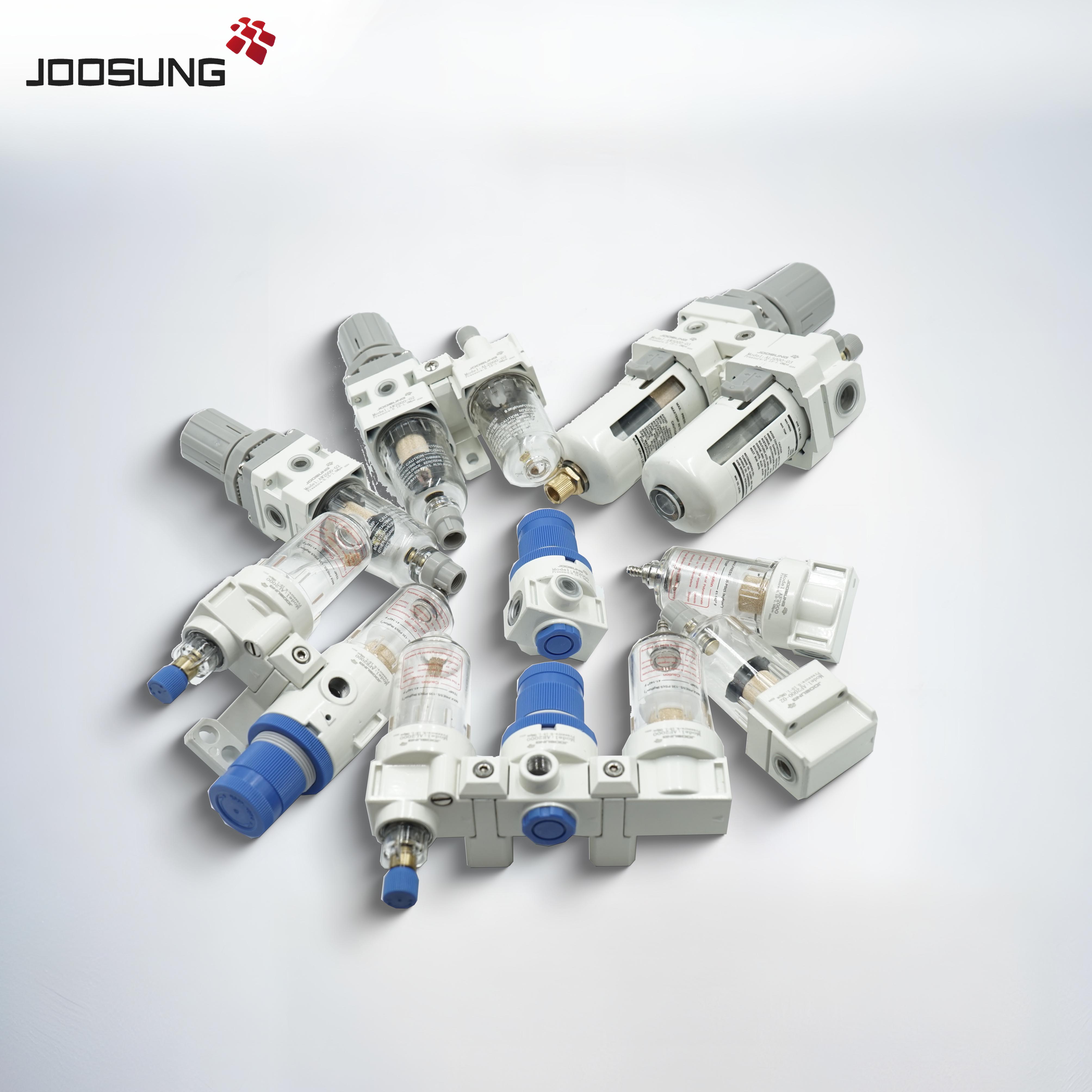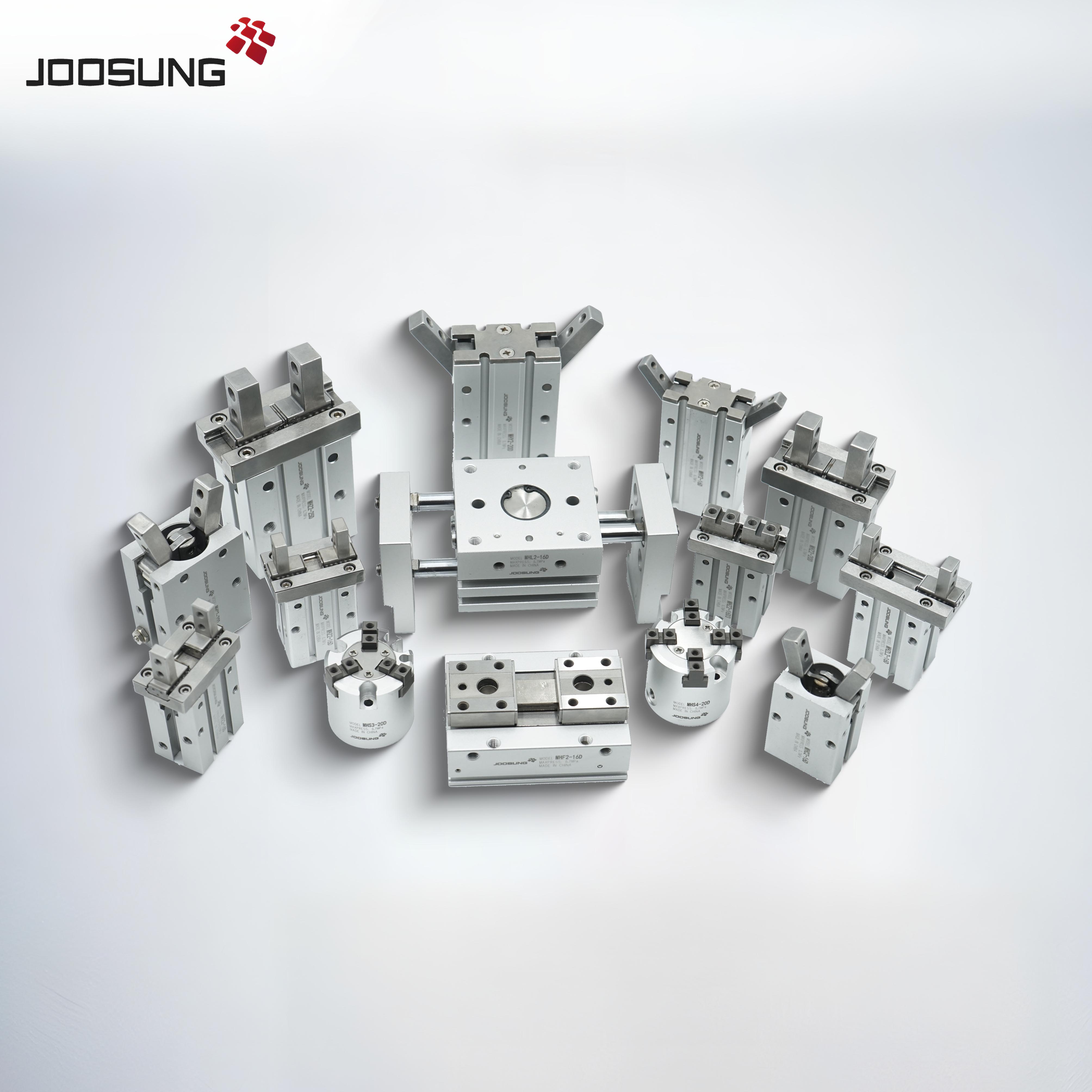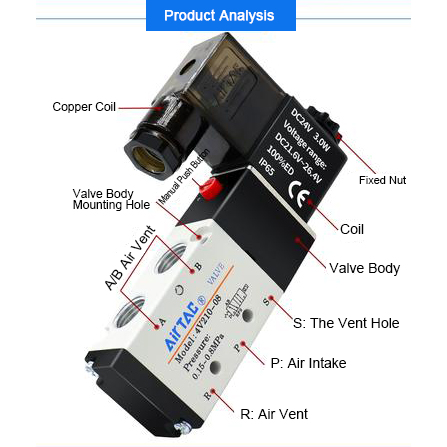
A pneumatic solenoid valve is a tool used to govern the drift of compressed air or gas in pneumatic systems. It makes use of an electrically operated solenoid to open, near, or direct airflow via the valve. those valves are commonly employed in industrial automation, manufacturing, and procedure control systems.
Key additives:
Solenoid: An electromagnetic coil that creates a magnetic discipline whilst energized, transferring a plunger to govern the valve's operation.
Valve frame: carries ports through which the air or gasoline flows.
Ports and Orifices: entry and go out points for the compressed air or gasoline.
Spring or Actuator: helps return the valve to its default function whilst the solenoid is de-energized.
working precept:
when the solenoid coil is energized, it generates a magnetic area.
This magnetic subject moves a plunger or armature, which either opens or closes the valve.
depending at the valve kind, this motion redirects airflow to extraordinary ports.
forms of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves:
2-way Valves: manage glide with the aid of beginning or remaining one direction.
3-way Valves: Direct waft among three ports for extra complex operations.
4-way or 5-way Valves: used in double-appearing cylinders to alternate airflow among two sides.
applications:
Automation systems: perform pneumatic actuators and cylinders.
business Machines: manage air supply in production device.
HVAC structures: alter air distribution in heating and cooling devices.
scientific devices: manipulate airflow in ventilators or laboratory device.
Their advantages encompass rapid response instances, precise manipulate, and compatibility with a huge range of running situations.