the principle distinction between 4/2 and 5/2 pneumatic valves lies within the variety of ports and the ways they manipulate the airflow in a pneumatic gadget. here's a breakdown of the differences:
1. quantity of Ports:
4/2 Valve:
It has four ports and 2 positions.
Ports are generally categorised as:
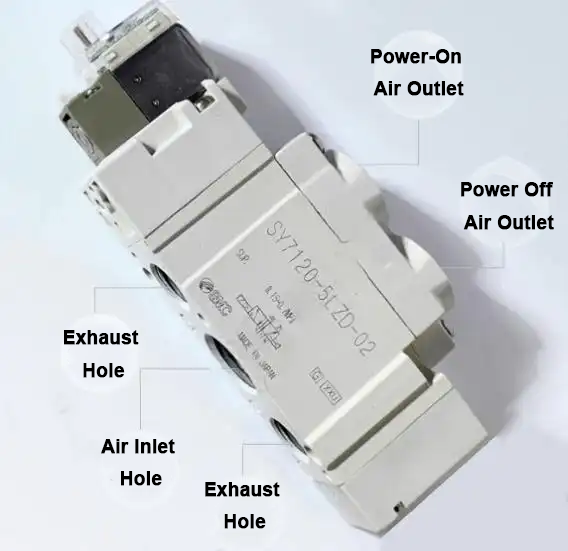
P (pressure): connected to the compressed air supply.
A and B: manipulate ports, related to actuators (e.g., cylinders).
Exhaust: Vent port for exhausting air.
The waft is directed to and from the actuator (or tool being controlled), and the valve controls the path of airflow to the actuator.
5/2 Valve:
It has 5 ports and 2 positions.
Ports are usually classified as:
P (stress): linked to the compressed air supply.
A and B: manipulate ports, linked to actuators (e.g., cylinders).
Exhaust Ports: normally 2 exhaust ports (often categorized as EA and EB) to release exhaust air while the valve shifts.
2. functionality:
4/2 Valve:
basically used for simple programs where a single actuator (such as a cylinder) is controlled in directions (enlarge/retract).
the two positions will both:
connect the P port to the A port (air into the actuator).
connect the P port to the B port (air into the opposite side of the actuator).
Exhaust: There’s commonly a single exhaust port that vents air to the surroundings whilst air is shifted in or out of the actuator.
5/2 Valve:
more versatile than the 4/2 valve, as it's far used in packages that require two exhaust ports (extra usually used with double-performing cylinders).
The 5/2 valve directs airflow to either port A or port B while also imparting separate exhaust ports for every route.
Exhaust ports: Separate exhaust ports (commonly EA and EB) are used, permitting the controlled exhaust of air from each facets of the actuator.
3. Use instances:
4/2 Valve:
often used for easy tasks wherein there’s no need for separate exhaust ports.
pleasant for controlling a unmarried-performing cylinder or situations wherein best one exhaust route is needed.
5/2 Valve:
typically used to manipulate double-performing cylinders, wherein ports are wished for every path of motion (one for each side of the piston).
utilized in extra complicated systems wherein exhaust control is important for controlling airflow direction and strain.
four. Exhaust control:
4/2 Valve: generally has 1 exhaust port.
5/2 Valve: Has 2 exhaust ports, which gives more control over the exhaust glide and is useful in packages requiring higher float control or double-appearing cylinders.
5. precis of variations:
| Feature | 4/2 Valve | 5/2 Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Ports | 4 Ports | 5 Ports |
| Positions | 2 Positions | 2 Positions |
| Exhaust Ports | 1 Exhaust Port | 2 Exhaust Ports |
| Usage | Simple actuation (single-acting) | More complex, double-acting cylinders |
| Applications | Simple directional control | Double-acting cylinders, complex flow control |
So, the 5/2 valve is generally more advanced, offering separate exhaust management and more versatility for controlling double-acting cylinders, while the 4/2 valve is simpler and suitable for less complex applications.